This article focuses on the analysis of the radiators currently used by UV LEDs, and summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of different types of radiators.
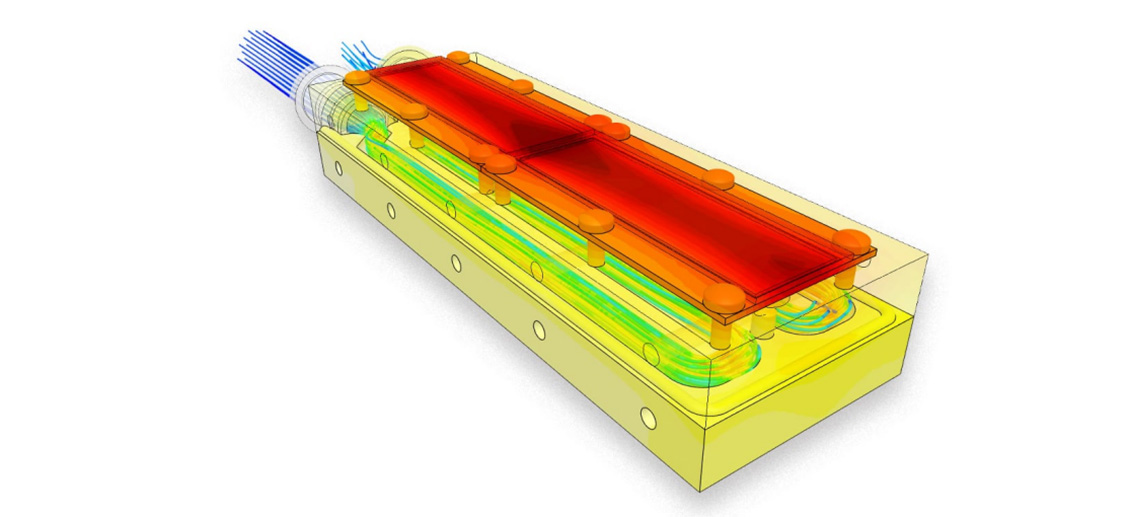
In recent years, the development and power increase of UV LED source have been remarkable. However, the progress is hindered by a crucial factor - heat dissipation. The rise in chip junction temperature negatively impacts UV LED performance, necessitating a focus on enhancing chip heat dissipation.
Radiators are essential components in UV LED system and come in various forms, including air-cooled radiators, liquid-cooled radiators, and new radiator technologies. Different heat sinks are suitable for different power UV LEDs.
Air-cooled Radiator for UV LEDs
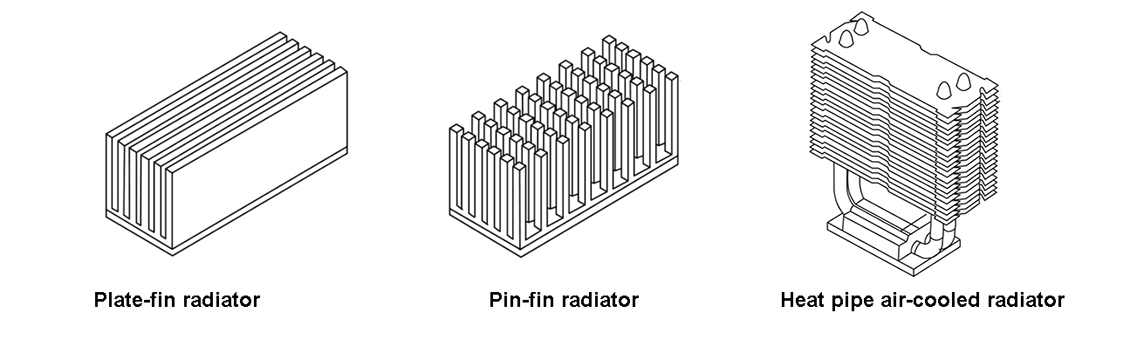
Air-cooled radiators for UV LEDs can be classified into finned and heat pipe-type. In recent years, air cooling technology has made significant advancements, allowing for higher power air cooling without compromising the chip's lifespan and reliability. Forced convection is commonly employed in high power UV LED. The shape and structure of the fins impact the heat dissipation performance, with plate and pin-fin structures being the most common types. Pin-fin structures offer better performance but are more prone to blockage. Heat pipes, as effective heat transfer devices, possess efficient heat dissipation characteristics.
Liquid Cooling Radiator for UV LEDs
Liquid-cooled radiators for UV LEDs utilize water pumps to drive liquid flow, offering high heat transfer capabilities. Active circulation cold plate radiators are fluid heat exchangers designed to cool UV LEDs, improving heat dissipation efficiency through optimized designs. Microchannel cooling, on the other hand, relies on multiple narrow channels to enhance heat dissipation efficiency, albeit posing challenges in channel structure design and manufacturing.
New Radiator
New heat sink technologies include Thermoelectric Cooling (TEC) and liquid metal cooling. TEC is suitable for low-power ultraviolet systems, while liquid metal cooling exhibits excellent heat dissipation performance.
Conclusion and Outlook
The issue of heat dissipation acts as a limiting factor in increasing the power capacity of uv curing led system, necessitating the combined application of heat transfer principles, material science, and manufacturing techniques. Air-cooled and liquid-cooled radiators are the main technologies utilized, while new heat sink technologies such as Thermoelectric Cooling and liquid metal cooling require further research. The research direction for heat sink structure design revolves around optimization methods, suitable materials, and improvements to existing structures. The selection of heat dissipation methods should be determined based on specific circumstances.
UVET Company is a manufacturer committed to providing high quality UV light. We will continuously research and optimize heat dissipation technologies, striving to improve the performance of system and offer high-quality products to customers.
Post time: Jan-03-2024

